HowTo: Shutdown VMware vSphere Cluster
In any virtualized environment, the availability and integrity of your ESXi cluster are paramount. While the robustness of modern hardware and software systems minimizes the risk of unexpected shutdowns, it is crucial to proactively plan for potential power outages or maintenance events. This blog post explores the importance of a well-executed VMware cluster shutdown, potential pitfalls to watch out for, the correct order of shutting down virtual machines, and solutions offered by OPMONis.

Inhalt:
Protect your VMware Cluster,
before the power fails!
Importance of a contolled Shutdown before Power Outage?
There are many reasons to perform a controlled and in time shutdown
Performing a controlled shutdown of a VMware cluster in the case of a power outage fundamentally helps protect and maintain the integrity of your system. This statement is based on the following facts.

- Data Integrity: Abrupt power loss can result in data corruption and inconsistencies. By initiating a proper shutdown, you allow virtual machines to save their state and ensure data integrity.
- Application Continuity: A graceful shutdown enables applications to conclude ongoing processes, maintain consistency, and avoid potential service disruptions or application errors upon power restoration.
- Hardware Protection: A controlled shutdown reduces the risk of hardware damage caused by power surges when power is restored.
- Time saving during restart: A proper shutdown avoids time-consuming repair and recovery actions of corrupt file systems or databases. Especially with a large number of virtual systems, this process can lead to a massive delay in resuming operations.
The usage of a UPS should be mandatory in this case. Further details to advantages of using a UPS can be found in the next section.
Using an UPS
Using an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to backup an VMware ESXi cluster offers several benefits. The obvious protection against short-term power failures and against overvoltage and undervoltage is only a small part of the advantages. We have composed all the other reasons for you here.
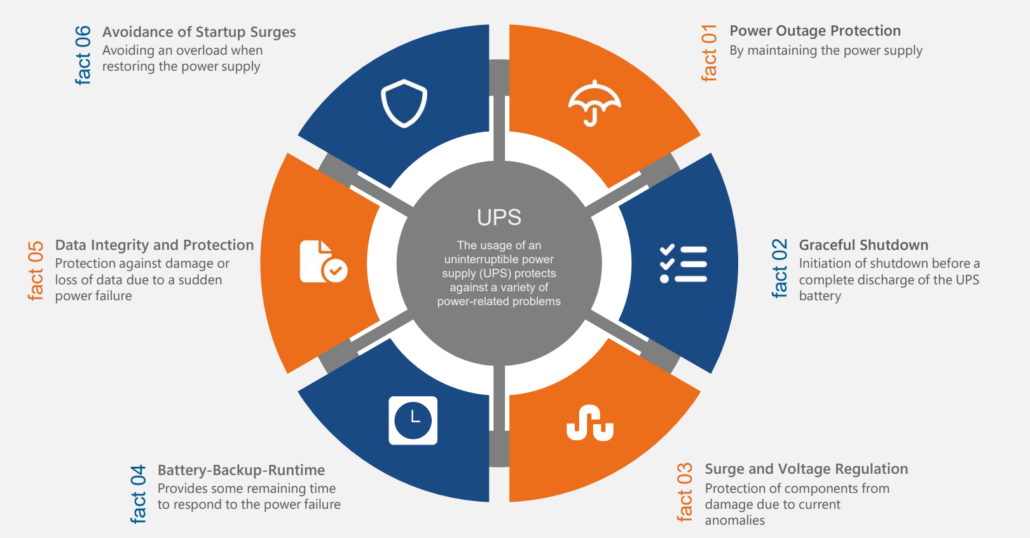
- Power Outage Protection: A UPS provides backup power during power outages or electrical disturbances. This helps prevent sudden shutdowns or disruptions to the ESXi hosts and virtual machines running on them. By ensuring a continuous power supply, a UPS helps maintain the availability and uptime of the cluster.
- Graceful Shutdown: When a power outage occurs, a UPS can send a signal to the ESXi hosts, notifying them of the power loss. This allows the hosts to initiate a controlled, graceful shutdown of the virtual machines. Graceful shutdowns help prevent data corruption, maintain the integrity of running applications, and minimize the risk of data loss.
- Surge and voltage regulation: A UPS typically includes surge protection and voltage regulation capabilities. It helps protect the ESXi hosts and other infrastructure components from power surges, spikes, and voltage fluctuations. These electrical anomalies can damage hardware components and lead to system failures. The UPS acts as a buffer, providing stable and clean power to the cluster equipment.
- Battery Backup Runtime: UPS systems are equipped with batteries that provide a certain amount of backup runtime. This gives you a window of time to react to a power outage, gracefully shut down virtual machines or even start a backup power generator if required. The runtime of the UPS depends on factors such as the power load, battery capacity, and configuration..
- Data Integrity and Protection: Sudden power loss can lead to data corruption or loss in virtual machines and storage systems. By using a UPS, you can ensure that critical data is protected and prevent potential data inconsistencies or system errors caused by abrupt power interruptions.
- Avoidance of Startup Surges: When power is restored after an outage, there can be a surge of electricity as devices power back on. This surge can strain the hardware components. A UPS can help mitigate this by providing a controlled and gradual power restoration to the ESXi hosts, reducing the risk of damage during the startup process.
Overall, using a UPS with an ESXi cluster helps safeguard against power-related issues, ensuring the availability, integrity, and proper shutdown of virtual machines and infrastructure components. It provides an extra layer of protection and helps maintain the stability and continuity of your virtualized environment.
Shutdown VMware vSphere Cluster
Whether the reason is a long lasting power outage and the resulting complete discharge of the UPS battery, or simply maintenance work for optimization or troubleshooting. We recognized that there are important reasons to prepare for a VMware Cluster Shutdown in a timely and comprehensive manner. For this reason, we here go into detail about the necessary steps, the potential pitfalls, and the topic of sequence and dependencies.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Shutting Down a VMware Cluster
Shutting down a VMware vSphere cluster is not complicated in principle, but to avoid unnecessary problems during the shutdown or the subsequent restart, a certain protocol must be followed. Since on a cluster there is usually a complex system with interdependent virtual machines, this protocol can vary from installation to installation. From a general point of view, however, it consists of the following steps.

- Connect to the vCenter Server management interface by typing in your browser the URL
https://Appliance-IP-Adresse-oder-FQDN:5480 - Log in with appropriate credentials.
- Select the cluster from the inventory view.
- Perform shutdown of the assigned virtual machines so that they are not moved to another host.
- Navigate to the “Hosts” tab.
- Select all the hosts on the cluster.
- Right-click the selection and select “Shutdown” or “Enter Maintenance Mode”.
- If you select “Shutdown”, the hosts are shut down immediately.
- If you select “Enter Maintenance Mode”, virtual machines that are still running will be migrated to other hosts in the cluster or shut down properly if no other hosts are available to host the virtual machines.
- Shut down any hosts that are still running and are now in maintenance mode.
- Confirm the action and wait for the hosts to shut down or enter maintenance mode.
- Once the hosts have shut down or entered maintenance mode, the VMware cluster is effectively shut down.
In the case of a power failure, the UPS helps to avoid a direct failure of the systems. However, due to the constant discharging of the UPS battery, there is usually little time to react. Therefore, an automation of the steps to shutdown a cluster is mandatory. How OPMONis can support you here, you will learn in the section “Use of an automation software: OPMONis”.
Pitfalls of a VMware vSphere Shutdown
Shutting down an ESXi cluster is unavoidable, as described in the cases of the previous sections. The basic steps and sequence have been described in detail and can serve as a first draft protocol. However, when planning and creating a custom shutdown checklist for your specific VMware cluster, be aware of the following potential pitfalls..

- Improper Shutdown Order: Virtual machines may have dependencies on other VMs or services. Failure to follow the correct shutdown order can result in service disruptions or data corruption. Prioritize shutting down dependent virtual machines before those that rely on them.
- Impact on running services: Shutting down an ESXi cluster will result in the powered-off state of all virtual machines running on the hosts. This can potentially disrupt critical services or applications. Ensure you have communicated and planned for any necessary downtime with the appropriate stakeholders.
- VM Migration Issues: If you choose to enter maintenance mode instead of shutting down immediately, the virtual machines will be migrated to other hosts in the cluster. However, if the cluster does not have enough resources or if there are any issues with the migration process, some virtual machines may fail to migrate or experience performance degradation.
- Resource Availability: Ensure that the remaining hosts in the cluster have enough resources (CPU, memory, storage) to accommodate the virtual machines that are being migrated from the hosts being shut down. Insufficient resources can impact the performance and availability of the migrated virtual machines.
- Network and Storage Considerations: Verify that network and storage configurations remain intact during the shutdown. Improper configurations can lead to connectivity issues or difficulty accessing storage resources.
- Storage Access: If your ESXi cluster is using shared storage, make sure the remaining hosts have proper access to the shared storage resources after the cluster is shut down. Check the storage connections and configurations to ensure that virtual machines can access their required storage resources.
To learn how automating these steps can help you avoid these pitfalls, see the section “Using automation software: OPMONis”.
Correct Order and Dependencies
In the previous paragraph, the pitfalls of VMware Cluster Shutdown were described in detail. Since this subject area is often very complex with the determination and application of the correct sequence based on the dependencies, we will once again go into the most important points in the analysis and implementation.

- Identify Dependencies: Identify any interdependent virtual machines or services within the cluster.
- Prioritize Dependent VMs: Start by shutting down the VMs that are not dependent on any other services or virtual machines. .
- Sequential Shutdown: Proceed with shutting down the virtual machines in a sequential manner, considering dependencies between them. Ensure dependent services or VMs are powered off after their dependencies are safely shut down.
- Finalize with Infrastructure Components: Once all virtual machines are shut down, proceed to safely shut down the cluster hosts and any other infrastructure components.
Who turns off the lights?
After clarifying all the details of a protocol for shutting down your VMware cluster, there is still the question of who is left as the last instance at the end, or who terminates the last system with the most dependencies. In practice, this is usually a centralized storage, where it is self-explanatory that this must also be shut down properly.
Below are several approaches with a description of the shutdown dependency when using an automation software and a storage.

- Shutdown storage with delay: After all dependent systems have been shut down, only the instance of the automation software and the storage system remain. The automation uses the interface provided by the manufacturer (or an external script) to issue the shutdown command for the storage system with a time delay and then shuts itself down. After the time delay has elapsed, the storage system shuts down.
- Dedicated Hardware for the Automation Software: The automation software runs on a system with dedicated hardware (baremetal) and its own hard disk. This allows the automation to initiate and monitor the storage shutdown and shut itself down at the end.
- Observe the peculiarities of the storage systems: In principle, it is not possible to give a generally valid recommendation for the procedure and timing of the storage shutdown. Too many criteria depend on the specific technical implementation of the storage system of the various manufacturers..
Are you looking for a solution to this problem and still have open questions?
We are happy to support you here to find a suitable solution for your individual situation.
Use of an Automation Software: OPMONis
Automation software must therefore monitor the UPS and shut down the system landscape in a timely and orderly manner in the event of a power failure. This results in the following list of requirements for the automation software:
- Monitoring of one or more UPSs
- Independence through the support of different UPS manufacturers or even the mixing of UPS manufacturers
- Scalability through the support of a heterogeneous system landscape with a large number of systems
- Support of a VMware vSphere cluster, both for the virtual machines and for the nodes (ESXi hosts) of the cluster
- Automatic and timely shutdown (depending on UPS remaining time or capacity)
- Attention to the dependencies in the shutdown order
- Reliability by waiting and checking for a complete shutdown, as well as error handling during shutdown so that a single system cannot block the overall process
- Clear display of the shutdown configuration with a easy-to-use User Interface
- Encrypted storage of all security-critical information such as user, password, and script content
OPMONis offers you a solution for all of the above!
OPMONis: Step by step explanatory video for the Configuration of a VMware cluster
In this video we show you a step by step tutorial how to configure a network UPS and a VMware Cluster in OPMONis.
Free 14-Day Trial Version
See for yourself and get your free 14-day trial today.
Contact
Do you have further questions on this topic or would you like specific advice on how OPMONis can help you in your specific situation?


