Why it is so important to do a reliable shutdown of virtualized systems in case of a power outage
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization roughly means the separation of an IT service and its components from the provision of the underlying physical hardware. Before the advent of virtualization in the IT sector, a single operating system was installed per computer, leading to a strong coupling of the software and the hardware. Problems were possible conflicts when running multiple applications on the same computer and often underutilized computer resources and an inflexible and very costly infrastructure.
Through the technical availability of virtualization, an independence between operating system and computer hardware could be achieved. Virtual machines are in their function and presentation identical to the installation on a real computer, but independent of the used hardware. Thus a virtual machine encapsulates the complete operating system with all installed applications in one unit.
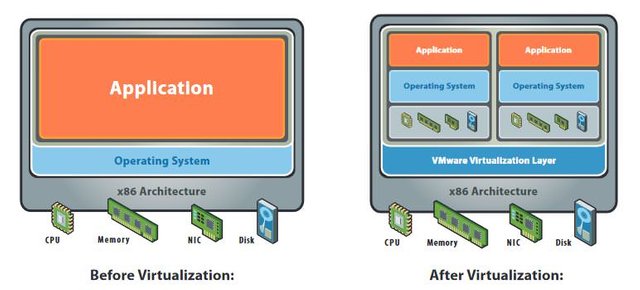
Image left without virtualization, Image right uses virtualization, Imagesource: https://www.vmware.com/pdf/virtualization.pdf
Benefits of Virtualization
IT managers and administrators are constantly faced with conflicting requirements. On the one hand there is the constant challenge of a cost-effective use of existing IT infrastructure. On the other hand, customers expect quickly response to business reorientation and flexibility in adapting to organizational changes and regulatory requirements. Virtualization offers the opportunity to provide contemporary solutions for fast changing requirements.
Cost savings through efficient use of resources
There are cost savings due to a smaller demand for physical hardware and decreasing costs for energy consumption in terms of power and cooling. On the other hand, there are additional expenses for acquiring the virtualization software as well as tools for ensuring smooth operation. In direct comparison to the purchase of countless new hardware this financially beats less.
Scalability and increasing flexibility
A really huge advantage is the better scalability of the systems and the increasing flexibility in adapting to changing business processes and market requirements. The addition of new hardware and new virtual servers is accelerated and simplified through a unified management environment. This leads to shorter waiting times for the potential users of new systems. Furthermore, the power supply can also be adapted dynamically during operation to the load curves and thus to the user behavior.
Increased efficiency and availability
Combining multiple virtual machines on a few physical systems automatically increases the required performance per hardware, resulting in improved overall hardware utilization. This also has a positive effect on the availability of the overall system, since in the event of a failure or maintenance on a single physical server, the virtual hardware can be automatically moved to a second physical hardware. The virtual machine thus continues to run without disruption and the users do not experience downtime. If defective hardware has to be replaced and the data restored, this no longer has to be done on a identical hardware.
With fewer physical systems, backup and recovery is less complex and financially affordable. The use of snapshots, which “represent an image of the state of a virtual machine at a specific time”, is also suitable here. Via a snapshot, e.g. the complete state of a virtual machine is conserved during operation and stored on a storage medium. The snapshot can thus be used as a fast backup before installing new operating system or software updates or as a system copy for the construction of a temporary test environment.
Sustainability
Lower energy consumption automatically means reduced CO2 emissions. On the one hand, this effect results from the consolidation and better utilization of the hardware and, secondly, from the associated reduction in waste heat and the required air conditioning technology. Reduced space requirements, despite increasing power delivery, can extend the life of existing data centers and potentially eliminate the need to expand or rebuild a data center.
Prevent the risk of data loss during extended power outages
The most important measure to avoid power failures and data loss is the use of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Short power failures in the range of seconds are bridged by these, so that a connected system is not affected in its operation. However, problems are to be expected in case of long lasting power outages. Here the use of power management software is a must to avoid data loss during extended power outages.
The operating system of a computer must be shutdown properly so that running applications and services can persist their changes and cached data and close any open files. Since stored data is partially kept in the cache of the hard disks for the purpose of optimizing access, these system components must also be given the opportunity to properly persist their cached data. In general, the write operations must not be interrupted as this can lead to inconsistent data, corrupt file systems and thus to serious problems on restarting the system.
Since in virtualized system environments usually several virtual servers run on one physical server, a power failure also affects several virtual machines. The virtual file system here represents an additional layer with its own cache. The persistence of the data of this layer is thus to be ensured from the point of view of several virtual machines. Furthermore, through virtualization the virtual machine no longer knows the hardware. If using a RAID controller (redundant array of inexpensive disks) with its own hardware cache, the operating system or the application (for example a database server) is no longer able to ensure the physical write (write through). Increasing cache sizes and a lack of protection of the hardware cache by an integrated battery have an even greater impact in the event of a power failure.
The consequence is that the operation of a UPS alone is not enough. In addition, appropriate software must ensure the contemporary and proper shutdown of the systems before the UPS has completely discharged.
OPMONis helps
OPMONis monitors your UPS and automates the contemporary and proper shutdown of your virtualized systems (VMware ESXi, HyperV and XenServer) during long lasting power outages.
OPMONis works independently of UPS manufacturer and thus works for all common models of all manufacturers.


